Module SOAP
- Prérequis
- Description
- Installation et configuration du module SOAP
- Configuration dans DigDash
- Lexique
- Références
Ce document décrit la connexion à une source de données en interrogeant un service web SOAP.
Prérequis
- Les acronymes utilisés par la suite sont référencés dans le lexique, à la fin de ce document.
- Disposer du dossier <digdash_installation>/add-ons/soap contenant l’application web nécessaire à la mise en place des appels vers des Web Services SOAP depuis DigDash. L’installation de cet add-on sera décrit dans ce document.
- Avoir en possession la liste des fichiers WSDL correspondant aux Services auxquels nous voudrons faire appel.
- Connaître un minimum la structure des requêtes SOAP (en XML) des méthodes à appeler, une documentation du Fournisseur des Services (que DigDash ne fournit pas) peut être nécessaire.
- Connaître les formats des valeurs des paramètres des requêtes SOAP à renseigner, une documentation du Fournisseur des Services (que DigDash ne fournit pas) peut être nécessaire.
Description
Généralités
DigDash propose la possibilité de récupérer des sources de données en interrogeant des services web SOAP.
Les échanges SOAP se faisant via des messages au format XML, le but est de pouvoir récupérer les réponses SOAP au format XML du service web et des les utiliser directement en tant que sources de données XML que DigDash sait traiter.
Pour ce faire, DigDash travaillera principalement avec les interfaces des services web, les fichiers WSDL que vous devrez fournir. Ceux-ci fournissent en effet une description détaillée de ce qu’offrent les services web à appeler.
DigDash se base sur l’API Java du fameux client SOAP, SOAP UI. La logique et la manière d’interroger le web service souhaité sera assez semblable, dans le sens où il faudra renseigner les valeurs des paramètres des requêtes.
D’où, comme indiqué en prérequis, la nécessité de connaître un minimum la structure de la requête SOAP au format XML.
Description technique
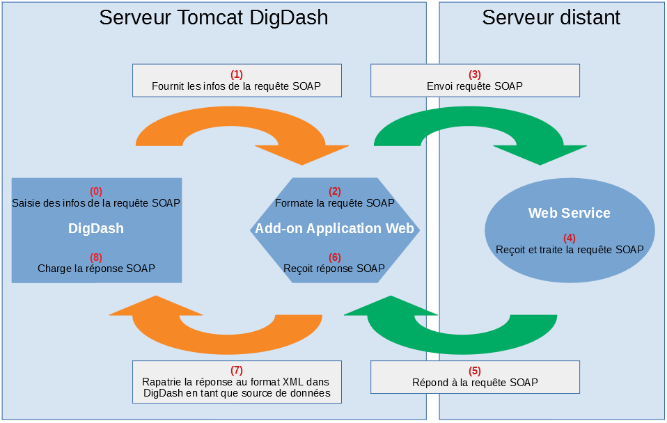
DigDash propose cette fonctionnalité en tant que module (ou add-on) à installer au produit (il n’est pas installé nativement). Il n’y a donc pas de source de données type « web service », mais on utilisera le principe existant dans DigDash des fichiers WLNK pour héberger les informations nécessaires à la récupération des données via SOAP.
Dans DigDash, vous ne devrez pas faire appel directement au point d’entrée du service mais passer par une application web (déployable sur le même serveur Tomcat DigDash) que DigDash a mise au point et qui constitue principalement l’add-on. C’est cette application web qui va se charger d’envoyer la requête SOAP avec les informations que vous aurez fournies dans DigDash et c’est elle-même qui se chargera de rapatrier la réponse SOAP dans DigDash.
Installation et configuration du module SOAP
Installation et déploiement de l’application web
- Arrêtez avant tout le serveur DigDash.
- Copiez l’application web ddsoap.war située dans le dossier <digdash_installation>/add-ons/soap vers le dossier <digdash_install>/apache-tomcat/webapps.
- Redémarrez le serveur DigDash pour déployer l’application.
Dossier wsdls
Dans le dossier <digdash_installation>/add-ons/ddsoap/wsdls, placez la liste des fichiers WSDL (.wsdl) correspondant aux descriptions des services que vous souhaitez interroger.
Configuration du fichier soap_props.properties
Dans le dossier de l’application déployée, configurez le fichier ddsoap/soap_props.properties comme suit :
Propriétés diverses
| Propriétés | Description |
|---|---|
| PRINT_DEBUG | Cette propriété doit être à true pour l’affichage des autres traces. Seules les traces d’erreur sont tout le temps affichées. Cette propriété permet d’afficher dans les logs les traces de debug. |
| SHOW_REQUESTS | Permet d’afficher les requêtes SOAP envoyées au Web Service. |
| SHOW_RESPONSES | Permet d’afficher les réponses SOAP envoyées par le Web Service. |
| LOGIN_BEFORE_CALL_SERVICE | Permet d’opérer une authentification avant l’envoi de la requête grâce aux propriétés identifiants (préfixées de _creds voir partie suivante). |
| REMOVE_REQUEST_EMPTY_VALUES | Supprime les valeurs vides (identifiées par des « ? ») de la requête SOAP. |
| REMOVE_REQUEST_EMPTY_NODES | Supprime les nœuds vide de la requête SOAP. |
Propriétés identifiants
Il est possible qu’une authentification soit nécessaire avant de faire appel à une méthode de service.
TOUTES ces propriétés doivent être préfixées de « creds_ » ET la propriété LOGIN_BEFORE_CALL_SERVICE doit être à ‘true’ (voir III.3.1).
| Propriétés | Description |
|---|---|
| Attention : les caractères spéciaux doivent être échappés dans les noms des propriétés (\= pour = , \: pour :) | |
| creds_binding | (Obligatoire) Le nom du service qui permet de s’authentifier. |
| creds_operation | (Obligatoire) Le nom de l’opération d’authentification. |
| creds_<username> | L’éventuel login pour l’authentification. |
| creds_<password> | L’éventuel mot de passe pour l’authentification. |
| creds_<any other parameter> | Les éventuels autre paramètres permettant l’authentification. |
Configuration dans DigDash
Création du fichier WLNK
Nous allons partir sur le procédé classique d’une extraction de données à partir d'un fichier au format XML.
- Depuis l'onglet Modèles du Studio, cliquez sur le bouton Nouvelle modèle.
- Dans la boite Création d'un nouveau modèle de données, cliquez sur le bouton Tous types de la section Fichiers.
- Sélectionnez le serveur de documents à utiliser.
- liquant sur le bouton Ajouter un fichier...
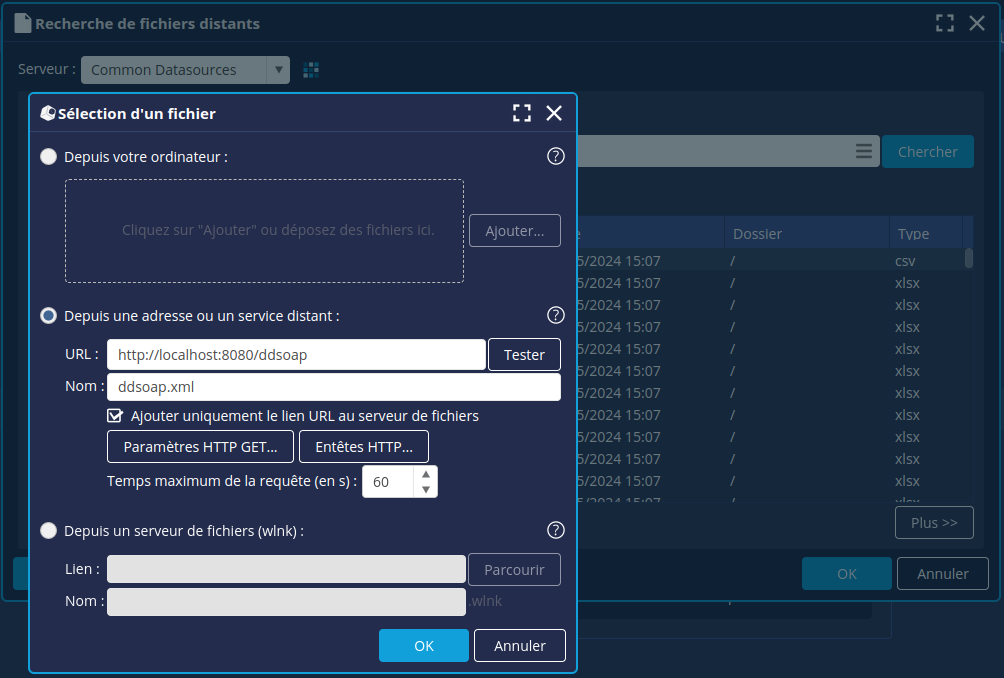
- Trois options sont disponibles. Pour récupérer du contenu via SOAP, nous allons utiliser l’option Depuis une adresse ou un serveur distant
- L’URL à appeler est celle de l’application web ddsoap précédemment déployée (<adresse_serveur_digdash>/ddsoap)
- Le nom du fichier WLNK doit finir par .xml
- Cocher l’option Ajouter uniquement le lien URL au serveur de documents. C’est cette option qui crée un fichier WLNK.
- Il est possible de personnaliser le Temps maximum de la requête (en secondes) dans le cas d’un WLNK (seules les valeurs > 0 seront prises en compte, sinon c’est le timeout par défaut qui est appliqué).
Vous pouvez renseigner les paramètres pour la requête SOAP sous forme de clé-valeur dans les paramètres GET HTTP:
- Cliquez sur le bouton Paramètres HTTP GET... puis entrez le nom et la valeur de chaque paramètre.
Vous devez OBLIGATOIREMENT renseigner au minimum ces deux paramètres :
_binding : le nom du Service à appeler
_operation : le nom de l’opération ou méthode du Service à appeler.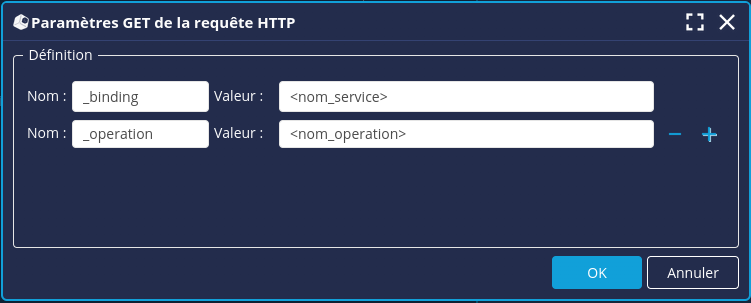
Pour les autres paramètres SOAP, il faudra mentionner leur nom (ne pas oublier les espaces de nommage s’il y en a). Si plusieurs paramètres apparaissent dans la requête, renseigner les noms des parents permettant de parvenir au nœud voulu.
En général, le premier nœud de la requête avec le nom spécifié sera sélectionné, à moins que le chemin pour accéder à un nœud spécifique est spécifié (en remontant dans les parents, sans pour autant remonter jusqu’à la racine).
| Séparateurs | Description | Exemple |
| / | Séparateur de chemin dans l’arborescence XML. | <a> <a1> <b>?</b> <c>?</c> </a1> <b>?</b> <c>?</c> </a> <a1> <b>?</b> <c>?</c> </a1> Pour accéder à l’élément c, on écrira a/c (c sélectionnera le premier élément c) |
| @ | Pour accéder à un attribut d’un élément XML. | <a> <b>?</b> <c attr=?>?</c> <a> Pour accéder à l’attribut attr de l’élément c, on écrira a/c@attr (ou c@attr directement) |
Une fois les paramètres SOAP saisis, cliquez sur OK pour valider.
➡ Le document WLNK sera créé et déposé sur le serveur de document sélectionné.
Ce fichier WLNK pourra ensuite être chargé en tant que source de données XML de manière classique.
Gestion de la pagination
Le module SOAP peut vous aider à agréger les données d’une requête paginée pour récupérer dans DigDash la totalité des données.
Pour cela, vous devez obligatoirement spécifier les paramètres GET suivants dans l’URL :
_pagination : ce paramètre doit être à true pour spécifier un cas de pagination.
_pageTag : vous devez spécifier dans ce paramètre le nom du tag (il peut s’agir d’un élément ou d’un attribut) qui définit la pagination (voir le tableau : Convention de nommage pour accéder à un nœud pour définir ce paramètre).
_pageStartElement : il s’agit du nom de l’élément englobant les lignes de données qui nous intéressent (voir partie suivante). Si vous ne connaissez pas la structure de la réponse SOAP, il vous faudra en général envoyer une première requête sans pagination dans un premier temps pour connaître le nom de ce tag (voir le tableau : Convention de nommage pour accéder à un nœud pour définir ce paramètre)..
_pageInc : l’index de la page commence à 0. Ce paramètre définit l’incrémentation de cet index.
_resultSize (facultatif) : spécifier le nombre de résultat total permet d’optimiser le temps de réponse.
Configuration de la source de données XML
Le chargement de la réponse SOAP au format XML en tant que source de données dans DigDash peut être difficilement lisible au premier abord.
Il faut en effet apporter quelques précisions à la configuration de la source de données DigDash pour que cela soit plus lisible.
Par exemple : si on considère une réponse SOAP avec la structure XML suivante :
<soapenv:Body>
<a></a>
<structs>
<struct1>
<s11></s11>
<s12>
<s121></s121>
</s12>
<s13></s13>
<s14></s14>
</struct1>
<struct2>
<s21></s21>
<s22>
<s221></s221>
</s22>
<s23></s23>
<s24></s24>
</struct2>
<struct3>
<s31></s31>
<s32>
<s321></s321>
</s32>
<s33></s33>
<s34></s34>
</struct3>
</structs>
</soapenv:Body>
</soapenv:Envelope>
Nous devons tenter d’identifier la structure englobant les structures (les lignes) qui nous intéressent. Dans cet exemple de réponse SOAP, les structures struct1, struct2, struct3 sont celles qui nous intéressent.
La structure englobant celles-ci est la structure structs.
Il faudra donc préciser dans la configuration du mdoèle de données, dans les options avancées de la sélection de données :
- Cliquez sur le bouton Avancé de la section Sélection des données.
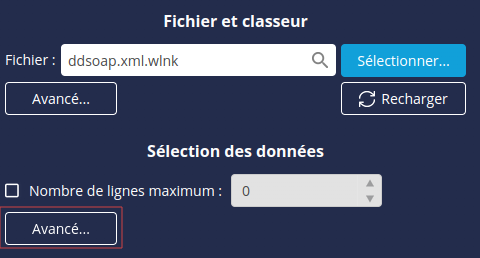
Cochez l’option Commencer la lecture du XML à partir d’un tag spécifié et précisez à partir de quelle structure commencer la lecture du XML.
On préférera aussi décocher l’option Déplier les nœuds fils et les attributs en colonnes.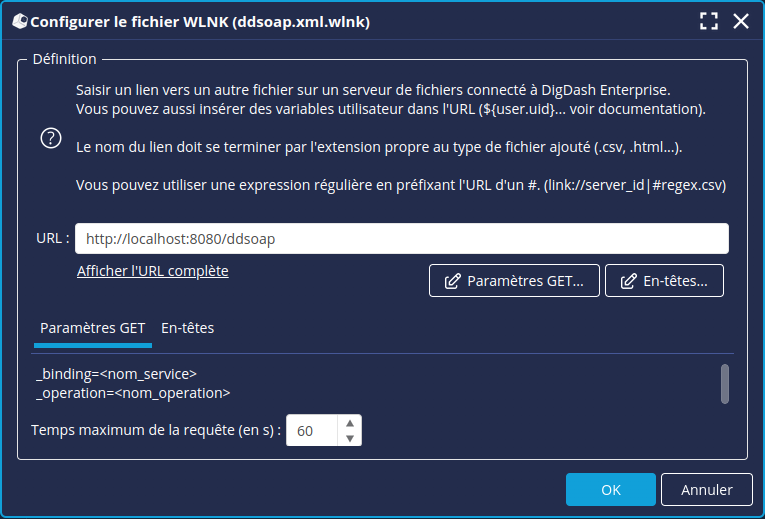
Cliquez sur OK.
Lexique
Nous appellons dans ce document :
- SOAP : Simple Object Access Protocol. C’est un protocole d'échange d'information structurée dans l'implémentation de services web bâti sur XML. (Wikipédia)
- WSDL : Web Services Description Language. Il s’agit d’un fichier au format XML permettant de décrire un service web.
- WLNK : Web LiNK. Les fichiers dont l’extension est .wlnk comportent des liens vers des sources de données.
Références
DigDash utilise la librairie OpenSource soapui de SmartBear Software pour supporter les échanges avec les services web SOAP.